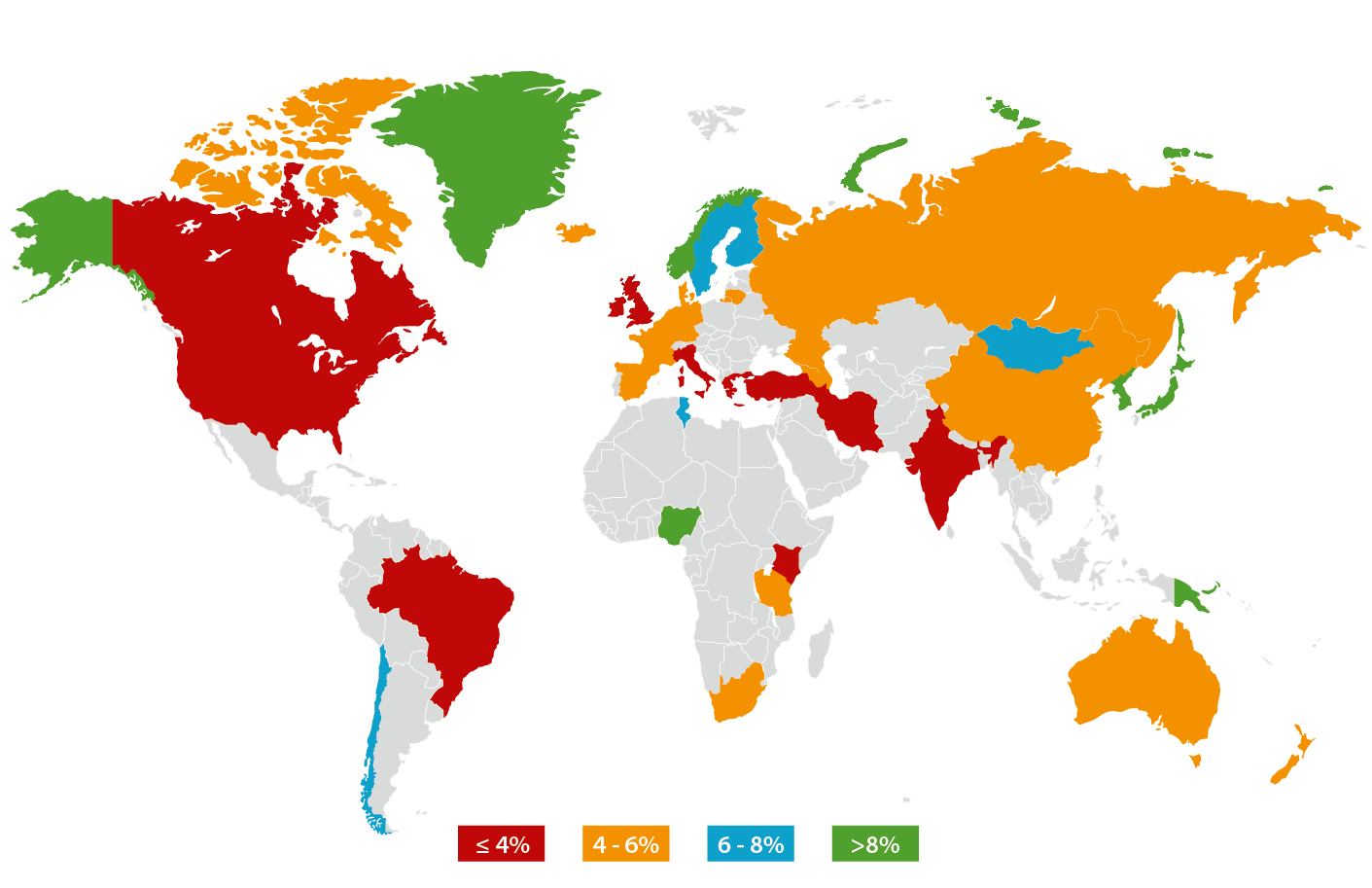
Ever wondered about omega-3 fatty acids? What do they have to do with inflammation? Why should you care about the omega-3 index? In this comprehensive article, we’ll dive deep into these essential nutrients and how they influence our bodies, especially our brains. We’ll also explore the importance of maintaining a healthy omega-3 index and the consequences of deficiency.
The Power of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammation
Our well-being greatly depends on omega-3 fatty acids. So, what’s the big deal about them? Inflammation holds the answer.
Our bodies react to injury or infection with inflammation. However, when persistent, it spells trouble. By controlling specific molecules, like eicosanoids and cytokines, omega-3s help manage inflammation. These tiny players have a significant impact on our body’s inflammatory response.
Now, let’s discuss inflammation markers: the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. High ratios and CRP levels? Often, they signal chronic inflammation and health risks. For optimal health, experts agree on a balanced omega-6 to omega-3 ratio. Yet, the average western diet boasts a 15:1 ratio, far from the ideal 3:1 or 1:1.
But wait, are all omega-3s the same? Let’s investigate further!
Omega-3: A Trio of Nutrients
Omega-3 fatty acids: what are they all about? Well, three types exist: ALA, EPA, and DHA. Despite falling under the same category, their bodily functions vary quite a bit.
Brain health and other functions? That’s where DHA and EPA come in. Sadly, our bodies can’t produce much of these fatty acids (DHA, in particular). So, we rely on our diets—fatty fish being a top choice.
But ALA? That’s another ball game. Our bodies can create ALA from other sources, like linolenic acid. This process involves enzymes such as delta-6-desaturase, which turns linolenic acid into ALA. But changing ALA into DHA and EPA? Not so efficient.
While our bodies can make some EPA and even less DHA from ALA, it’s insufficient. That’s why eating DHA and EPA-rich foods or taking supplements is crucial.
But what about the omega-3 index? Why should it matter to us?
Understanding the Omega-3 Index
What’s the omega-3 index, and how is it measured? It’s all about EPA and DHA levels in red blood cell membranes, expressed as a percentage of total fatty acids. A higher index? Often linked to a lower risk of heart disease and other health concerns.
So, what makes the omega-3 index so vital? It’s an accurate way to evaluate a person’s omega-3 status. A healthy index helps lower inflammation, boosts brain function, and enhances overall well-being. Interestingly, a 2008 study revealed that an omega-3 index above 8 cut the risk of acute coronary syndrome by a staggering 69% (check out Figure 1!)

A multitude of elements, like age, genetics, and diet, can impact the omega-3 index. By grasping these factors and tweaking as needed, you’ll be able to boost your omega-3 levels and enjoy the health perks that come with it.
A Look at Omega-3 Deficiency in the US
Many people in the US are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. To give you an idea, Figure 2 provides you with an illustration of the average omega-3 index values from the US and Japan.
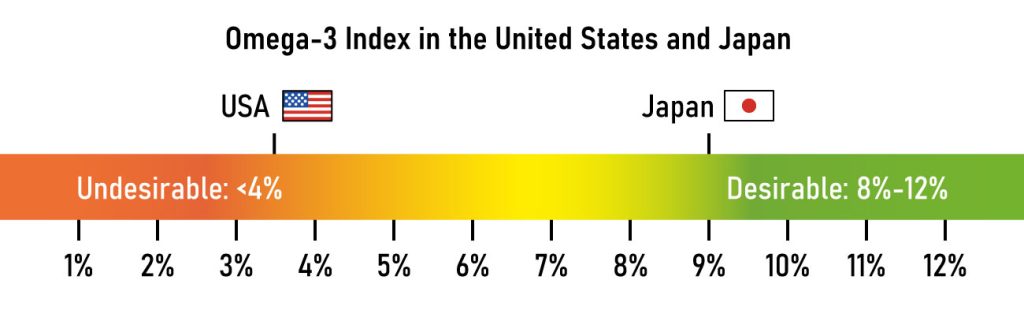
The results are quite alarming. Independent experts usually suggest an omega-3 index of at least 8% for peak health. However, the average values in the mentioned studies fall noticeably below (USA) and well above (Japan) the recommended mark. The fish consumption of the average Japanese individual and the prevalence of omega-6 fatty acids in US cuisine (think burgers, fries, and burritos) help explain this. This deficiency in the US leads to many consequences, like a higher risk of heart issues, cognitive decline, and mood disorders.
Wondering how to enhance your omega-3 levels?
Boosting Your Omega-3 Intake
Boosting your omega-3 index requires consuming more foods or supplements rich in EPA and DHA. Some tasty EPA and DHA sources include:
- Tasty fatty fish (think salmon, mackerel, sardines, herring)
- Fish oil supplements
- Algae-based supplements (great for vegetarians and vegans)
- Fortified foods (like omega-3 enriched eggs, milk, yogurt)
Moreover, adding more ALA-rich foods to your meals helps since your body can change small ALA amounts into EPA and DHA. Some ALA sources are:
- Flaxseeds and their oil
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Canola oil
Don’t forget: consistency matters. Regularly incorporating omega-3-rich foods in your diet helps maintain a healthy omega-3 index.
Measuring Your Omega-3 Index
Want to discover your omega-3 index? Here’s the scoop.
The omega-3 index test, a straightforward blood test, measures EPA and DHA levels in red blood cells. Visit a healthcare expert or try an at-home kit. Generally, the process includes a finger prick for a tiny blood sample, later sent to a lab for examination.
With your omega-3 index results in hand, you can make educated choices about diet and supplements to boost your levels. Monitoring your omega-3 index is a wise strategy for staying healthy.
Achieving an Optimal Omega-3 Index: The Role of Supplementation
How can you reach an omega-3 index of 10 through optimal supplementation of EPA and DHA? A study from 1999 indicates that increasing your daily intake of EPA and DHA by as little as 1000mg could result in an omega-3 index of approximately 9.5%. However, experts generally recommend consuming a daily combination of 3000-4000mg of DHA and EPA through both diet and supplementation to achieve optimal levels.
Keep in mind that acquiring these crucial fatty acids via a balanced diet is the ideal intake method. By grasping the significance of EPA and DHA supplementation and making knowledgeable decisions on daily consumption, you can strive for a healthier omega-3 index and improved overall wellness.
GLA: The Unsung Hero of Fatty Acids
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) is an essential fatty acid. It boasts potent anti-inflammatory effects. However, it’s merely one of five crucial health-enhancing fatty acids in our meals. ALA (omega-3, extracted from flaxseed oil), EPA (omega-3, derived from fish or algae oil), and DHA (omega-3, sourced from fish oil and algae) are other examples. GLA (omega-6, primarily present in borage oil) and oleic acid (omega-9, mainly in olive oil, but also in flaxseed and borage oils) are also vital. Researchers recognize these as indispensable for our well-being.
Fascinatingly, these fatty acids deliver distinct health perks, and swapping one for another won’t work. For instance, fish oil consumption won’t offer GLA’s benefits and could even trigger GLA deficiency. Conversely, GLA alone may reduce EPA levels and raise pro-inflammatory arachidonic acid. Yet, pairing fish oil with borage oil avoids these problems. Likewise, relying solely on ALA (from flaxseed oil) might not enhance DHA status and could even diminish oleic acid. Thus, when using flaxseed oil, it’s smart to also supplement with fish oil, olive oil, and borage oil.
Additional Tips for a Healthy Lifestyle
While it’s crucial to maintain an optimal omega-3 index, achieving overall wellness involves more than that. Here are some extra tips to help you embrace a healthier lifestyle:
- Follow a low-carb Paleo diet: Embrace a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including non-starchy vegetables, low-sugar fruits, high-quality proteins from grass-fed and pasture-raised animals, and healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, and avocado. Aim for a well-rounded diet that focuses on whole, unprocessed foods, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients while minimizing carbohydrates.
- Stay active: Engage in regular physical activity to keep your body strong and fit. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise.
- Get enough sleep: Prioritize sleep to support your body’s natural healing and recovery processes. Most adults need 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga, to help keep your stress levels in check. High stress levels can negatively impact your immune system and overall well-being.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support your body’s vital functions. Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining healthy skin, digestion, and energy levels.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of chronic diseases and negatively impact your overall health. Quit smoking, and if you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Healthy Vitamin D level: make sure your vitamin D bloodserum value is about 50ng/mL. You can achieve that by exposing your skin to the sun or supplementing with vitamin D.
By incorporating these healthy habits into your daily routine, you can further improve your well-being and complement the benefits of maintaining a healthy omega-3 index.
Final Thoughts
The omega-3 index is a valuable indicator of our health status and a vital tool for monitoring and managing our omega-3 levels. With a widespread deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, it’s crucial to take charge of our omega-3 intake and make informed decisions about our diet and supplementation. By understanding the significance of the omega-3 index, adopting healthy habits, and striving to maintain optimal levels, we can enhance our overall health and pave the way for a brighter, healthier future.
Conclusion
In summary, omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA (but also GLA), are very important for our health. They play a critical role in regulating and reducing inflammation in our body, and supporting brain function. Therefore, the omega-3 index is an essential tool to assess and monitor our omega-3 status. With many people in the US showing deficiencies, it’s more important than ever to pay attention to our omega-3 intake and ensure we maintain a healthy omega-3 index (i.e. > 8%) for overall well-being. By understanding the significance of the omega-3 index and taking proactive steps to improve our levels, we can pave the way for a healthier future and a better quality of life.